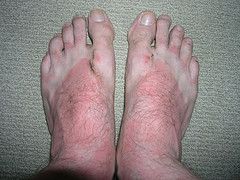
Sunburn occurs when your skin is burned by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Sunburn, whether mild or severe, can cause permanent skin damage and increase the risk of wrinkles, freckles, pigmentation, skin lesions, and skin cancer including malignant melanoma.
Whilst we need some exposure to sunlight for Vitamin D production, we don’t need sunburn! In an Australian summer, sunburn can occur within 15 minutes. Skin burnt by UV radiation turns red within hours and the sunburn will continue to develop for the next one to three days. Most people who have been sunburnt will also peel. This is the body’s way of healing and shedding dead and damaged skin cells to make way for new skin underneath.
Farming men, women and agricultural workers are at an increased risk of sunburn as they spend more time working outdoors during peak UV times.
UV radiation levels vary depending on location, time of year, time of day and cloud coverage. The UV index scale tool is a great way for farmers and agricultural workers to check peak UV times during the day and the times sun protection is required. The UV index scale can be accessed by downloading the Sun Smart app on a smartphone or the Bureau of Meteorology website.
Recommendations to prevent sunburn include a combination of five sun protection measures:
- Slip on long clothing,
- Slop on SPF50+ sunscreen,
- Slap on a broad-brim hat,
- Seek shade
- Slide on sunglasses.
Ensure sunscreen SPF 50+ is available in the workshop, work vehicles and machinery. Apply sunscreen 20 minutes before sun exposure to allow time for the sunscreen to absorb and reduce the likelihood of dust sticking to your skin.
Skin damage from sunburn can be mild or severe. To relieve mild discomfort drink plenty of water, gently apply a cool compress and take over-the-counter pain relief.
Seek medical advice if you experience nausea, fever or there is extensive blistering and pain.
Find out more at Better Health Channel
Fast facts:
- Even minor sunburn can lead to skin damage and skin cancer.
- Sunburn can occur in less than 15 minutes.
- Protect your skin – limit exposure, especially in the middle of the day. –
- Use SPF 50+ broad-spectrum sunscreen that filters both UVA and UVB radiation.
- Wear long sleeved shirt and long trousers and a broad brim hat.
- Protect your eyes with AZ/NZS compliant sunglasses with fitted side arms.
- Where possible seek shade and plan indoor activities for the middle of the day.
References used for this topic
More information:
Cancer Council Australia
Vitamin D
What happens when your skin gets sunburnt?
Sunscreen
Skin cancer
Sunsmart
UV & sun protection
Sun protection for babies and toddlers
Workplaces
Clinical care:
Safer Care Victoria
Burns
Research & reviews:
The Medical Journal of Australia
Estimates of beneficial and harmful sun exposure times during the year for major Australian population centres
Preventive Medicine Reports
Farmers sun exposure, skin protection and public health campaigns: An Australian perspective
World Health Organization (WHO)
Ultraviolet radiation and human health
|
|