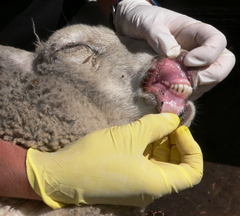
Scabby mouth is a disease caused by a virus that is common in sheep and goats and some other ruminants. This disease is referred to as contagious ecthyma, or orf in humans. Scabby mouth is very contagious among sheep and is most commonly detected by a scab appearing on the mouth, muzzle, teats, legs or feet (see photo).
Farmers and farm workers can catch scabby mouth when they have an abrasion that comes into contact with infected animals. They can also be infected accidentally when handling the Scabby mouth vaccine. Human-to-human transmission is extremely rare.
Once infected, people usually have lifetime immunity. No medical treatment is required for this virus. Normal wound management – keep the wound clean and covered – will see the orf heal in 4-6 weeks.
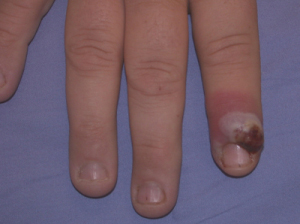
Symptoms in humans
- Red papules or lesions, usually on hands or arms (under the armpit for shearers from holding feet under their arms)
- Low fever (sometimes)
Lesions usually heal without treatment, but sometimes they can become infected. This is a particular concern for people with compromised immune systems.
People who have dermatitis, which is common among farmers, may get large lesions that are slow to heal.
Treatment
- For healthy people, keeping the wound clean and covered is usually enough.
- Antibiotics are not necessary unless a secondary bacterial infection occurs.
Prevention
- Avoid handling sheep with scabby mouth
- Wear latex gloves if you must handle infected animals
- Cover your scratches and cuts when you vaccinate sheep or goats
- Consider wearing rubber gloves when you vaccinate animals for scabby mouth
- Wash the area immediately if you accidentally come in contact with the vaccine
- Wash all exposed skin with soap and water – do not use a scrubbing brush as it can cause a break in the skin and introduce the virus
Fast facts:
- Scabby mouth, also called orf, is a disease that farmers can catch from infected sheep.
- Scabby mouth causes pustules and lesions on the areas where skin contact has occurred with infected sheep.
- Take care when vaccinating animals, and wear gloves.
References used for this topic
More information:
Agriculture Victoria
Scabby mouth sheep
Department of Primary Industries (NSW)
Sheep Health – Scabby Mouth [PDF]
The Center for Food Security and Public Health
Contagious Ecthyma (2015)
Research & reviews:
Centres for Disease Control and Prevention
Human Infection with Orf Virus and Description of Its Whole Genome
Epidemiology and Infection
Erythema multiforme after orf virus infection: a report of two cases and literature review, 2015
|
|